Root Canal Treatment

What is Root Canal Treatment?
- An overview of RCT
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.”
Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. Root canal treatment is one type of endodontic treatment.
To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development.
The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it. Below you can learn more about exactly what a root canal is.

Stage 1: A Deep Infection
- Determining the extent of the infection.
Root canal treatment is needed when an injury or a large cavity damages the tooth’s pulp and root and the root becomes infected or inflamed.

Stage 2: A Route to the Root
- An opening is made in the tooth.
The dentist numbs the tooth. An opening is made through the crown of the tooth to the pulp chamber.

Stage 3: Removing the Infected and Inflamed Tissue
- The infection is cleaned and shaped for filling material.
Specialised files are used to clean the infection and unhealthy pulp out of the canals.
Then they shape the canals for the filling material. Irrigation or flushing is used to help clean the canals and remove debris.

Stage 4: Filling the Canals
- Canals filled with permanent material.
The canals are filled with a permanent material. Typically this is done with a material known as gutta-percha. This helps to keep the canals free of infection or contamination.

Stage 5: Rebuilding the Tooth
- Sealing the opening with a temporary filling.
A temporary filling material is placed on top of the gutta-percha to seal the opening.
The filling remains until the tooth receives a permanent filling or a crown.
A crown, sometimes called a cap, looks like a natural tooth.It is placed over the top of the tooth.
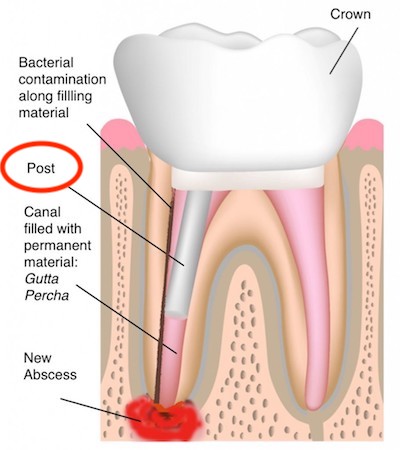
Stage 6: Adding Extra Support
- Additional support added through a post.
In some cases, a post is placed into the root next to the gutta-percha. This gives the crown more support.

Stage 7: The Crowning Touch
- The crown is cemented into place.
The crown is cemented into place.

Patient Consultation |

Fillings |

Dental Bridges |

Scaling and Polishing (Teeth Cleaning) |


